GitOps is a method for managing infrastructure and applications where you describe the desired state in a Git repository, using version control. It's particularly useful for teams that want to use continuous deployment. GitOps automates the process of deploying and managing code, reducing the need for manual communication, and increasing visibility and transparency in the development cycle. It helps teams improve their software delivery and monitoring through automation.
What is GitOps?
GitOps is a way to manage Kubernetes clusters and other cloud-native applications through a Git-based approach to infrastructure and app management. It uses a declarative model, where the desired state is defined in a Git repository and then automatically deployed to the appropriate environment. This separates the app, configuration, and infrastructure code for easier management and scaling.
With GitOps, everything is managed through Git, making it a single source of truth for deployments and reducing manual intervention. It automates deployment, minimizes errors, and simplifies version control. Specifically, for Kubernetes, when you create manifest files, GitOps will automatically apply them to the cluster once changes are made, eliminating the need for manual kubectl commands and speeding up the deployment process.
ArgoCD is a popular open source tool used to implement GitOps Practices.
Benefits of GitOps:
1.)Automation: GitOps automates the entire CICD Pipelines flow, so we do not need to execute any kubectl commands at the end of pipeline.
2)Version Control: Since we are using Git as a single source of Truth, everything will be available in Git and if you want to go back to earlier versions, it will be easy.
3)Consistency: Consistency is achieved across different environments, improving configuration reliability. You can have multiple environments managed by a single ArgoCD cluster having multiple branches in a GitHub repo or separate Github repos for different environments.
4)Security: GitOps enhances security by controlling access to Git repositories, ensuring authorized users make changes.
5) Faster deployments: Efficiency and faster deployment times are achieved through automation.
How GitOps works
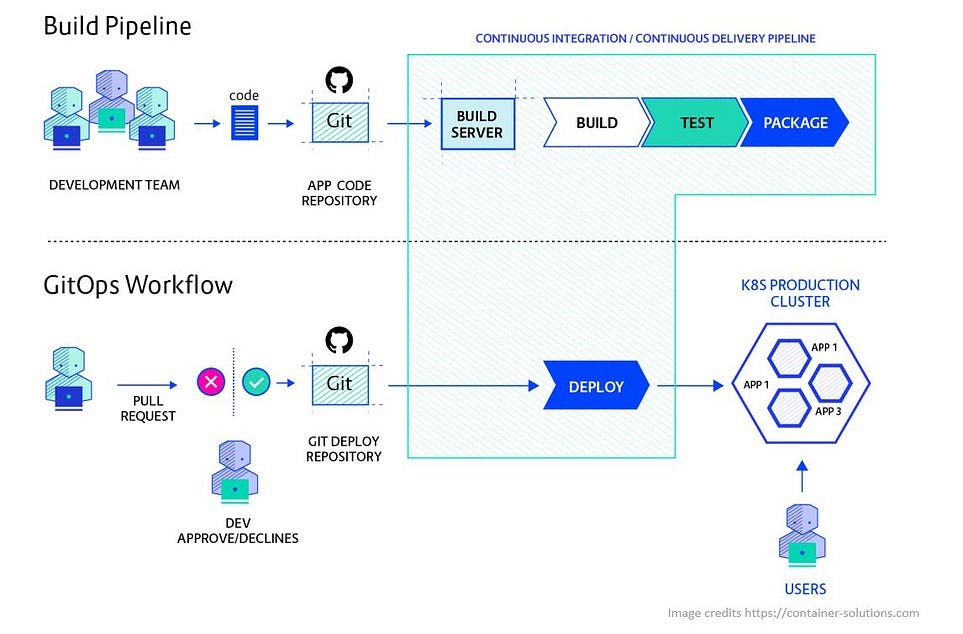
GitOps provides a clear definition of how the application and infrastructure should be designed and deployed. It follows a simple workflow that revolves around the Git repository, consistent declarative states and the use of automation to continuously apply configurations through pull-based pipelines.
GitOps workflow :
1.)The software development team commits their infrastructure and application code into a Git repository hosted in a source control management (SCM) system such as GitHub or GitLab.
2.)The GitOps operator continuously monitors the Git repository for new changes.
3.)When changes are detected in the repository, the GitOps operator applies the configuration using automation tools like Kubernetes, Terraform, or other configuration management tools.
4.)The GitOps operator then waits for the new environment to be updated to a healthy state.
5.)If changes are successfully applied, the new state of the infrastructure and application is stored in the Git repository. If there are any errors, changes are rolled back to previous versions automatically.
6.)Development teams can roll back changes at any time via Git, allowing them to quickly revert changes if necessary.
7.)This automated approach to deployment provides security, transparency, and traceability throughout the development cycle.
Implementing GitOps in software development
Hands-on:
Create a New Roles in AWS IAM with EKS-Cluster and EKS-NodeGroup use case.

Give a name and attach the service role which you have created in First step.
In next tab, select all default values for AMI, disk size and choose only t3.medium for instance type as ArgoCD requires instance types greater than that. Also select subnets and create NodeGroup.
# tetris-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tetris-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1 # You can adjust the number of replicas as needed
selector:
matchLabels:
app: tetris
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: tetris
spec:
containers:
- name: tetris
image: nasi101/tetrisv2 # Replace with the actual image tag
ports:
- containerPort: 80 # Replace with the port your Tetris game listens on
tetris-svc.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: tetris-service
spec:
selector:
app: tetris
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer
After NodeGroup is created, go to your command line interface and install kubectl on it. Once kubectl is installed, you need to connect kubectl with this cluster by using below command:
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name GitOps --region us-east-1
Once the connection is done, check whether connection is established properly by knowing pods, As nothing is configured on cluster, you will see No resources exists.
go to this link and enter all cli commands necessary to install ArgoCD.
https://archive.eksworkshop.com/intermediate/290_argocd/install/
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/v2.4.7/manifests/install.yaml
sudo curl --silent --location -o /usr/local/bin/argocd https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v2.4.7/argocd-linux-amd64
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/argocd
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}'
export ARGOCD_SERVER=`kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd -o json | jq --raw-output '.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname'`
export ARGO_PWD=`kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d`
The last 2 commands are for getting the Load Balancer DNS Name & storing that into ArgoCD Server and the password we will use for logging into ArgoCD Server.
LB DNS and password will be stored in ARGOCD_SERVER & ARGOCD_PWD variables respectively.
Now open LB DNS in a browser and you can see ArgoCD application running in that browser.

Login with Username as admin and password in ARGO_PWD variable and you will be able to login to the ArgoCD server.

Go to Manage your Repositories -> Repositories -> Connect your repo using HTTPS.
Once we connected our repo details, then create a new application with application name, git URL and cluster details such as cluster URL, namespace.. as mentioned in below pic.
Once application is created, you can see after few seconds that the application is healthy and synced.
You can check your pods using kubectl get pods command and you can see pods running as application is synced with ArgoCD.
Click on three dots on tetris-service and you can see Hostname and this is the server where your tetris-game application has been deployed.
Now comes the magic of ArgoCD, now try to replace the docker image to other version. Go to GitHub and change the image version from v1 to v2.
Now in ArgoCD, you can see that the new version has been synced and when you open endpoint in a new tab. You can find the new commit in the last sync result.
Now refresh the DNS and check whether you are getting the old version or newer one.
You have now used GitOps for automatically syncing with Kubernetes without the need to apply kubectl command everytime there is a change in deployment or other manifest files.
Thanks for reading