Artificial intelligence has recently significantly altered various sectors, and DevOps is among those affected. The increasing utilization of AI tools like ChatGPT has made prompt engineering a vital competency for professionals in the DevOps field.

This blog will explore the significance of prompt engineering and its relevance to DevOps. It will provide insights into how AI can be used to enhance infrastructure management, continuous integration, delivery pipelines, incident response, and beyond.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering refers to developing, designing, and optimizing prompts to enhance the output of Foundational Models for your needs. The prompt gives little guidance and leaves a lot to the model’s interpretation. The structure of the prompt frequently influences the quality of AI-generated responses. In the context of DevOps, prompt engineering can provide the automation of numerous tasks, help in troubleshooting efforts, generate automation scripts, and deliver immediate documentation, all achieved through carefully crafted input prompts.
Why Should DevOps Engineers Care About Prompt Engineering?
In the realm of DevOps, time is invaluable. Through the application of prompt engineering, one can:
On-Demand Code Generation: Automate the creation of documentation and code. Instantly generate scripts (consider tools such as Terraform, Ansible, Python, or Jenkinsfiles).
Faster Troubleshooting: Quickly compose alerts or responses to incidents.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Minimize repetitive work by offloading them to AI.
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI can recommend scaling infrastructure, improving deployment strategies, or optimizing resource usage based on detailed prompts.
Prompt engineering is a powerful technique for enhancing the efficiency of your DevOps processes.
Key Prompt Engineering Techniques for DevOps
This section examines techniques where prompt engineering can be incorporated into DevOps workflows to yield significant advantages.
| Technique | What It Does Do? | Example Prompt |
| Zero-Shot Prompting | Model answers without any prior examples. | “Write a Terraform code to create an EC2 Instance.” |
| Few-Shot Prompting | Provide a few examples to help the model understand the task. | “Here are two alerts: <examples>. Now write an alert for CPU over 90% usage.” |
| Chain of Thought Prompting | Guide the model through a multi-step task. | “First, explain Jenkins pipelines. Next, generate a Docker-based pipeline. Then show how to deploy it to AWS.” |
| System Prompts | Set the model’s behavior (e.g., instruct it to behave like a DevOps bot). | “Act as a DevOps Engineer. Generate Ansible playbooks for Apache server setup.” |
Prompt Engineering Techniques in Action (with Examples)
Zero-Shot Prompting (Quick Terraform Configuration): No need to search Google! Just ask the AI to generate a Terraform configuration.
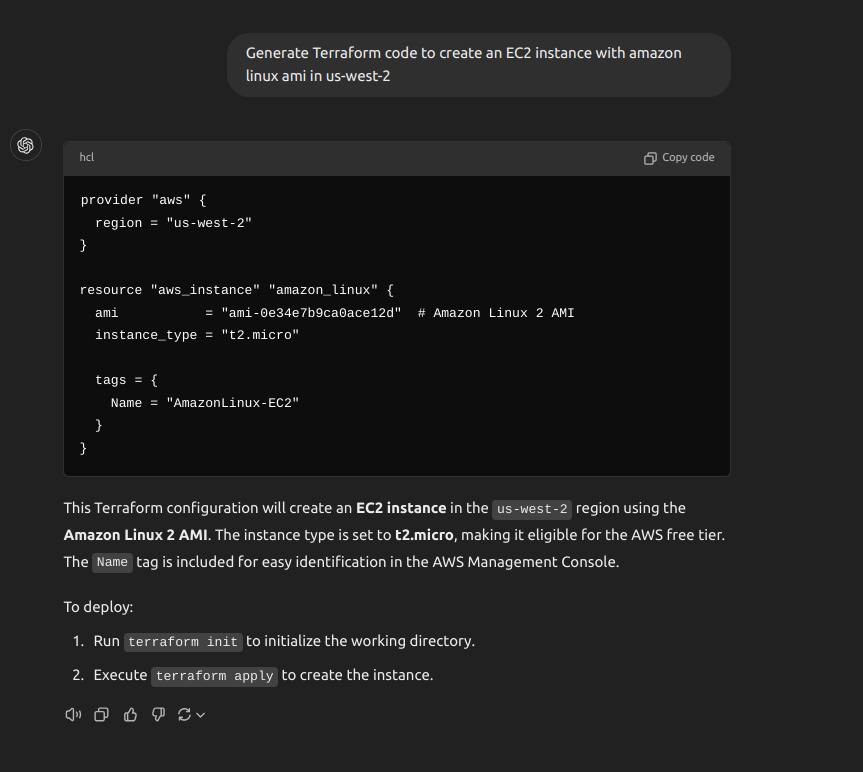
Zero-shot Prompt Engineering
Few-Shot Prompting: Incident Alert
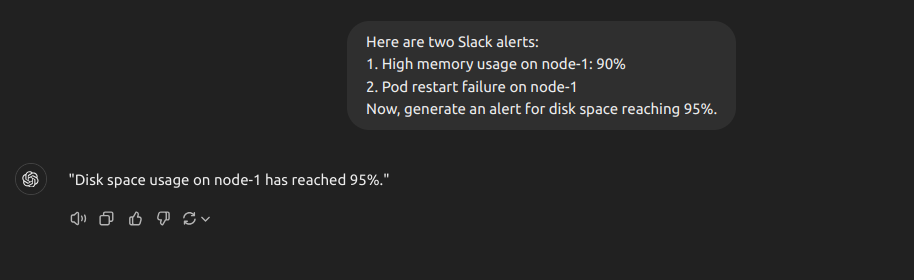
few-shot Prompt Engineering
Chain of Thought Prompting: CI/CD Setup Example.
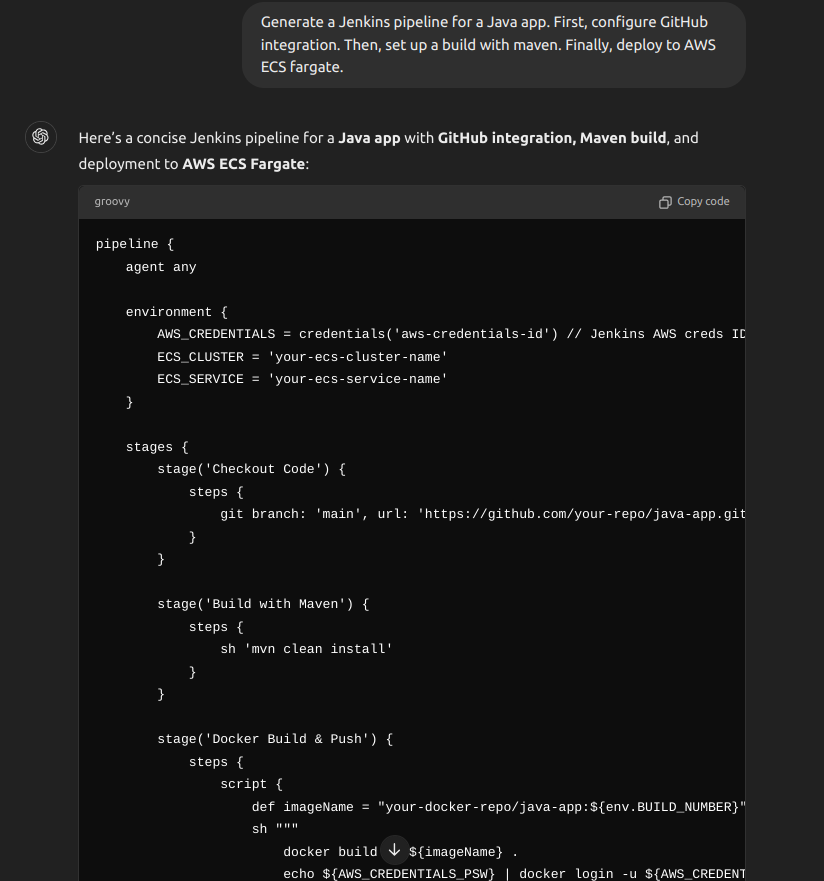
Chain of Thought Prompting

Chain of Thought Prompting
Best Practices for Prompt Engineering in DevOps
Be Precise: Random prompts may lead to incomplete or wrong responses. For instance, indicate the specific type of infrastructure, cloud service, or programming language required.
Provide Context: Start Giving context to your prompts, such as the environment (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP), version details, or particular configurations, to enable the AI to customize its response effectively.
Iterate and Improve: Achieving the ideal answer may not occur on the initial attempt. Experiment with various prompt formats and adjust them based on the feedback received to enhance the quality of the output.
Utilize Code Examples: If the AI has access to the context from an existing codebase or configuration file, it can generate more precise responses. Include relevant code snippets in the prompt to direct the AI’s focus.
Treat AI as a Collaborator, Not a Substitute: While AI-generated recommendations can be beneficial, it is essential to review and verify the output before implementing it in a production environment. Prompt engineering should serve to enhance your expertise rather than replace it.
AI as a Collaborator
Future of DevOps with Prompt Engineering
The integration of AI-powered prompt engineering with DevOps tools is just beginning. The future may look like this:
Automated Releases & Deployments: Deployments that are automated through natural language directives.
Systems that possess self-healing capabilities, identifying and rectifying problems independently.
Intelligent chatbots functioning as DevOps aides, managing daily routine responsibilities.

chatbots
Proactive Monitoring: AI-enhanced systems can foresee and address incidents before their effect on users, thereby minimizing downtime.
Natural Language Queries: Teams can inquire about infrastructure performance or deployment statuses using straightforward text commands.

NLP
AI-Assisted Learning: DevOps teams gain contextual insights and educational resources tailored to their specific environment and challenges.
Examples of prompts:
Write a guide for deploying a Python Flask web application on AWS using Elastic Beanstalk
Develop a script for automating server provisioning using Terraform for AWS infrastructure.
Create a CI/CD pipeline using Jenkins for continuous integration and deployment of a Node.js application.
Set up a Kubernetes cluster on AWS using EKS and deploy a containerized application.
Create an AWS Lambda function using Python to process incoming data from an S3 bucket.
Write a script to monitor the health of a cloud-based application on AWS using CloudWatch and send alerts.
Develop a Docker Compose file to run a multi-container application with a Node.js backend and MongoDB.
Set up a GitLab CI pipeline to automate the deployment of an application to Google Cloud Platform.
Create an Ansible playbook to configure web servers on multiple EC2 instances in AWS.
Write a Terraform script to provision an AWS S3 bucket and enable versioning and encryption.
Develop a solution for creating auto-scaling groups in AWS to ensure your application scales based on traffic.
Assist in configuring a Jenkins pipeline that deploys a web app to an Azure Web App service.
Write a guide for configuring Kubernetes Helm charts to deploy a scalable microservices application.
Create a script to automate the backup of databases in the cloud using AWS RDS and S3.
Design an approach for managing and automating infrastructure using GitOps with tools like ArgoCD.
Act as a DevOps Engineer and develop a Dockerfile and containerization strategy for a Java Spring Boot application. Ensure the Dockerfile includes all the necessary dependencies, build steps, and configurations for running the application in a containerized environment.
Act as a DevOps Engineer and evaluate the existing CI/CD pipeline for a Ruby on Rails project hosted on GitLab CI/CD. Provide recommendations to optimize the pipeline, such as parallelizing test suites, introducing canary deployments, and integrating code quality checks and security scans.
Act as a DevOps Engineer and create a containerization strategy using Kubernetes for a Python Flask application. The strategy should include defining deployment manifests, configuring load balancing, and implementing scaling policies based on resource utilization and traffic patterns.
Act as a DevOps Engineer and propose a scaling strategy for a mobile app deployed on Firebase Hosting to handle high user demand and ensure optimal performance. Consider leveraging Firebase features like hosting CDN, Firestore database sharding, and Cloud Functions auto-scaling.
Act as a DevOps Engineer and develop a tool or script for automating the deployment of a Node.js application to AWS Elastic Beanstalk. The tool should streamline the process of configuring the environment, deploying the code, and managing the infrastructure resources.
Act as a DevOps specialist and provide suggestions to improve the existing CI/CD pipeline for a Python Django project. The pipeline currently uses Jenkins for building, testing, and deploying the application. Identify areas for optimization, such as parallelizing tests, implementing deployment strategies like blue-green deployments, and integrating additional quality checks.
Act as a DevOps consultant and design a monitoring and alerting strategy for a mobile app deployed on the Google Cloud Platform. The strategy should include setting up performance monitoring, log aggregation, and defining alerts for critical metrics using services like Stackdriver or Prometheus.
Act as a DevOps expert and create a Dockerfile and containerization strategy for a Java Spring Boot application. The Dockerfile should package the application along with its dependencies, and the strategy should address efficient image building, optimization of container size, and integration with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
Act as a DevOps engineer and propose a scaling strategy for a web application deployed on Microsoft Azure. The strategy should focus on handling high-traffic loads and ensuring scalability. Consider utilizing features like auto-scaling, load balancing, and caching to achieve optimal performance and resource utilization.
Common commands for ChatGPT that might also be useful:
“Act as” — you can start a request by defining a role for the bot. This will help it better understand the context. It can be a profession, position, a famous personality, or even a console that indicates what code to output.
“Ignore Previous Commands” — since ChatGPT remembers all your conversations and the instructions you gave earlier, you can ask it to ignore them without starting a new chat.
“Step by Step” — ask the bot to respond sequentially to get a more elaborate, logical, and detailed response.
“Do not write your own opinion” — please refrain from adding your own opinion.
“Continue” — if text generation stops in the middle of a sentence, this command will continue the text from where it left off in the previous response.
“Summarize” — this command is useful when you need a concise overview of a topic or response.
“Compare & Contrast” — a command for comparing objects and identifying similarities and differences.
“Clarify” — if the artificial intelligence’s response is unclear or ambiguous, this command will help you get a more straightforward explanation.
“Brainstorm” — this command is handy when you require fresh ideas or innovative solutions.
Hope these ideas will help you with automating routine tasks in #DevOps.
Connect me on LinkedIn or make a clap if you found it useful.
Connect me on GitHub or make a clap if you found it useful.